Glass manufacturing process
Published date: 27 July 2022
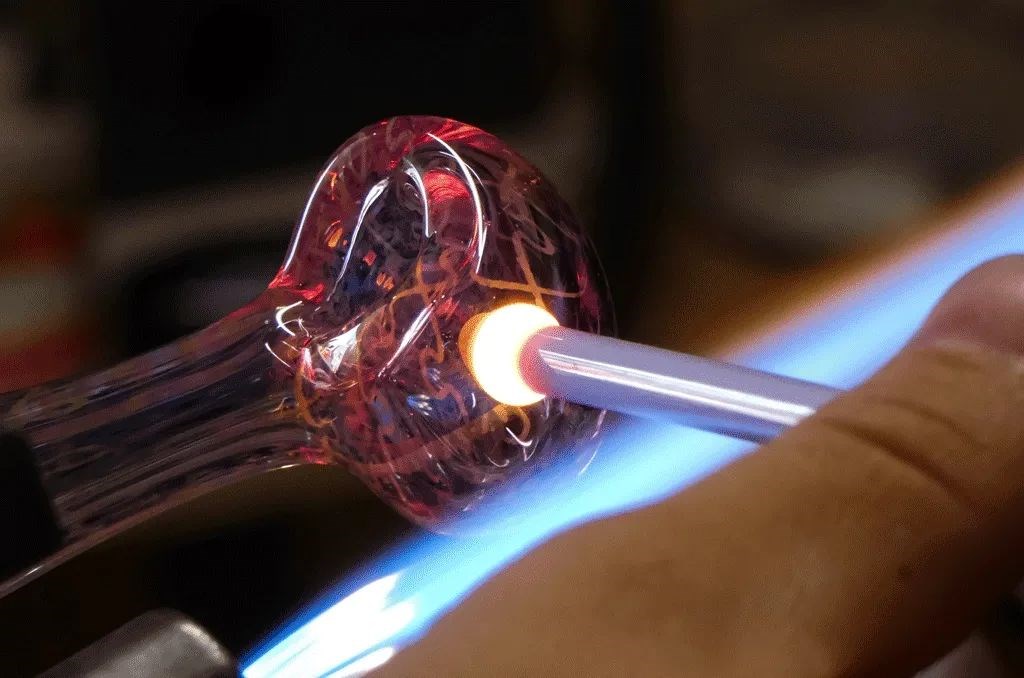
Glass is a solid, transparent material that is ubiquitous in everyday life. Its countless applications range from the practical, to the technological, to the decorative. Glass is made from melting raw materials such as sand, soda ash and limestone.
The glass manufacturing process has been refined over the course of thousands of years. Let’s have a brief overview of the procedure.
What materials are used in the glass manufacturing process?
Most of the glass used today is soda-lime glass. This type of glass is inexpensive, durable and extremely workable. Soda-lime glass is made of 70% silica. Soda (sodium carbonate) is added to lower the melting point. Calcium oxide from lime provides increased chemical durability. Alumina, dolomite and fining agents are also part of the manufacturing process.
Different types of glass can be produced with different materials to achieve specific properties. For instance, borosilicate glass uses boron trioxide. Borosilicate glass is resistant to thermal shock. It is used in cookware, lighting and more.
In addition to raw materials, cullet and decolourisers are also used in the glass manufacturing process. Cullet is recycled glass. It is employed to lower the melting temperature of glass, leading to energy saving and decreased costs. Decolourisers eliminate the green-yellow tint from the ferrous oxides present in the raw materials.
What steps are followed in the glass manufacturing process?
- Grinding and mixing. The base materials are powdered in grinding machines. Then, they are mixed in exact proportions. The resulting mixture is known as batch or frit.
- The batch is transferred to a furnace and melted at a temperature of about 1500°C.
- The molten glass is given shape at this stage. This part of the glass manufacturing process can either be done by hand or by machine. The main shaping processes are glassblowing (used to produce containers) and float bath (used to create glass sheets).
- Glassblowing: Air is blown through a pipe to blow the molten glass in the desired shape.
- Float bath: The glass is fed into a bath of molten tin. This creates a floating, thin “ribbon” with smooth surfaces on both sides and even thickness.
- Other shaping procedures: They include casting, pressing, drawing and spinning the molten glass.
- This is the procedure in which the glass items are cooled down slowly. It usually involves a thermally-insulated chamber. This is known as a lehr. Annealing is crucial to the glass manufacturing process. Glass that has not been properly annealed is likely to crack under stress.
- Quality check. The annealing is followed by strict quality checks on the finished products.
Conro Electronics is a leading supplier of materials and tools in the electronic manufacturing industry.
We’ll show you how to improve product reliability while increasing performance and lowering costs. Our team of technical support specialists will provide your company with dependable global supply, unrivalled efficiency, and superior technical support.
Feel free to contact us on 0208 953 1211 or send us an email to info@conro.com




Comments
There are currently no comments, be the first to comment.