Protecting printed circuit boards
Published date: 04 May 2023
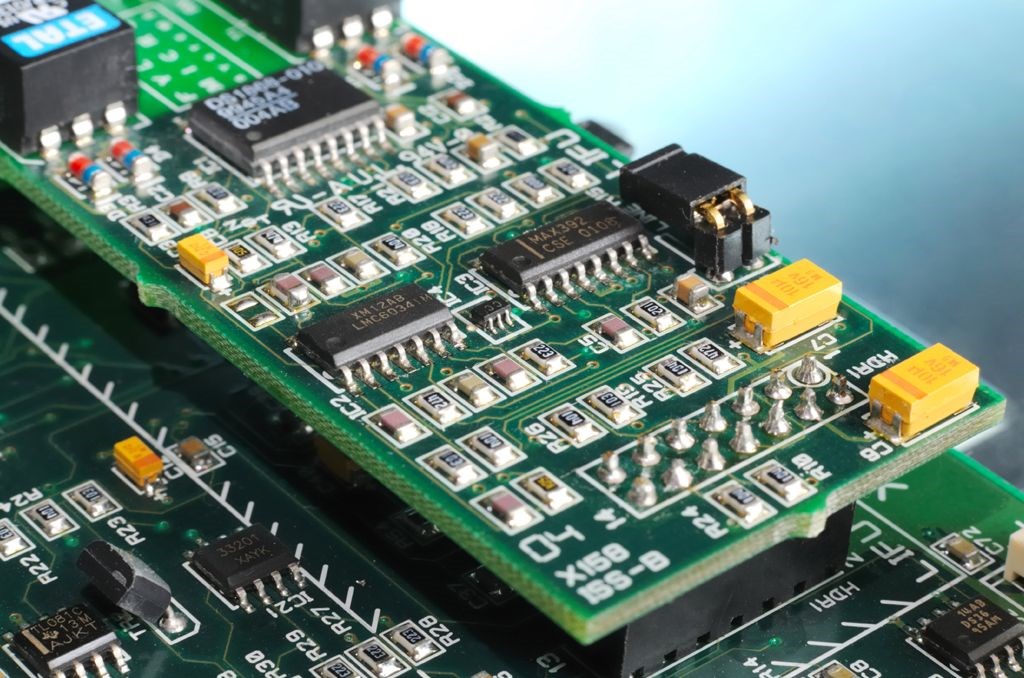
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics, providing the necessary connectivity and support for various electronic components. As these boards become increasingly sophisticated and delicate, it is crucial to ensure their protection from environmental factors, such as moisture, dust, and temperature swings. In this article, we will explore the importance of safeguarding PCBs and discuss some effective methods to shield these vital components from damage.
Understanding Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
Printed Circuit Boards, commonly referred to as PCBs, are thin boards made of conductive and insulating layers, with conductive pathways etched or printed onto their surfaces. PCBs act as a central hub where various components, such as resistors, capacitors and sensors, are securely mounted.
Today, PCBs are mass produced and widely used in numerous electronic devices, ranging from smartphones and computers to automotive systems and industrial equipment, playing a critical role in enabling the functionality of modern technology.
The importance of PCB protection
PCBs are vulnerable to various environmental factors that can compromise their performance and reliability. Moisture, for instance, can lead to corrosion of the conductive traces, resulting in faulty connections or complete failure. Dust and debris accumulation may cause short circuits or overheating, leading to irreparable damage. Temperature fluctuations can also cause expansion and contraction, stressing the PCB and potentially causing cracks or solder joint failures.
Protecting PCBs is important for a number of reasons. First, it ensures that the board’s functionality is not compromised by exposure to harmful conditions. Second, it can help prolong the life of components that are mounted on the board. Finally, it can reduce the risk of costly repairs or replacements.
Conformal coatings for PCBs
The most effective method of protecting PCBs is through the application of conformal coatings. These thin, protective films are designed to encapsulate the board, shielding it from moisture, dust, and other contaminants. They also offer protection against dangerous temperature fluctuations or extreme heat and cold. Conformal coatings provide a barrier that can be customised to suit specific environmental conditions.
Types of conformal coatings
Examples of commonly used conformal coatings include acrylics, silicone, urethanes, and epoxy. They can be applied in a number of ways, including brushing, dipping or manual/automated spraying.
- Acrylics: Acrylic conformal coatings offer good general protection and are known for their ease of application and repairability.
- Silicone: Silicone coatings provide excellent moisture and temperature resistance, making them suitable for demanding environments.
- Urethanes: Urethane coatings offer a balance between flexibility and protection, making them ideal for applications requiring resistance to chemicals and mechanical wear.
- Epoxy: Epoxy coatings provide robust protection against moisture, chemicals, and abrasion, ensuring high reliability in harsh environments.
Printed Circuit Boards play a pivotal role in the functionality of electronic devices, and protecting them from environmental factors is vital for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Conformal coatings offer effective protection against moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations, prolonging the lifespan of PCBs and safeguarding the integrity of electronic systems. By implementing these measures, manufacturers and users can enjoy the benefits of resilient and long-lasting PCBs in their electronic devices.
At Conro Electronics, we’ll show you how to improve product reliability while increasing performance and lowering costs. Our team of technical support specialists will provide your company with dependable global supply, unrivalled efficiency, and superior technical support.
Feel free to contact us on 0208 953 1211 or send us an email to info@conro.com




Comments
There are currently no comments, be the first to comment.